
MRI is useful in detecting stress reactions in the pars region, noted by intraosseous edema, prior to fracture. While pars defects can be seen on an MRI, sensitivity and specificity is not well established. That said, it is more common for an MRI to be the first advanced imaging study for a symptomatic patient. CT scans are the most sensitive imaging modality in detecting the presence of a pars defect. Flexion-extension radiographs may demonstrate dynamic mobility that may exist. The abnormality is classically described as a fracture of “the Scottie dog’s neck” ( Fig. In an effort to produce radiographs that are more sensitive, some advocate using a 30-degree oblique cranial tilt to demonstrate spondylolysis. In addition, Dr Lee is also proficient with intraoperative navigation for spinal surgery.Imaging of spondylolisthesis can begin with standard plain radiographs that include lateral, anteroposterior, and oblique views.

Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (TLIF).Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion (LLIF/XLIF).Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (ALIF).Multiple techniques exist for spinal fusion, these include: Spinal fusion is the joining of two or more spinal segments to prevent motion. Typically, surgical treatment of spondylolisthesis involves spinal fusion. Bone grafting of the fracture may also be performed during the surgery to encourage healing. The procedure involves inserting a screw across the fracture. Pars repair is performed when there is no slippage of the vertebrae. If non-operative treatment fails, then surgery may be required.ĭr Lee will discuss these treatment options with you during your consultation.Surgical treatment for patients with spondylolysis may include repair of pars or spinal fusion. Similarly, patients with spondylolisthesis may get better following a treatment plan of physiotherapy and lifestyle changes.

A period of rest and avoiding participation in any sporting activities may be advised following acute pars fracture, allowing time for the fracture to heal. Dr Lee may suggest a non-operative treatment plan for your condition. Most patients with spondylolysis and/or spondylolisthesis may improve without surgery. Numbness in the foot and weakness of the muscle supplied by the nerve may occur.ĭr Lee focuses on obtaining an accurate diagnosis before implementing treatment. When the slipped vertebra is severe, occasionally nerve roots can be stretched causing shooting pain down the back of the legs and into the foot. Spondylolisthesis occurs when the pars defect results in failure to maintain spinal alignment and the vertebra slips forwards out of normal position and over other parts of the spine.
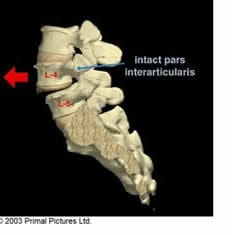
Spondylolisthesis is also commonly known as slipped vertebra. Symptomatically, patients experience pain of the lower back, extending down through the buttocks and hamstrings. Some patients may not be aware they have spondylolysis (pars fracture) until they have x-ray taken of their back. This condition is commonly seen in gymnast, dancers, athletes, cricket players and football players where a lot of stress is being placed on the pars. Pars fracture, also known as spondylolysis or pars defect, is a stress fracture or break involving the small inter-connecting part of the lumbar spine.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
